navy
791169701662408704
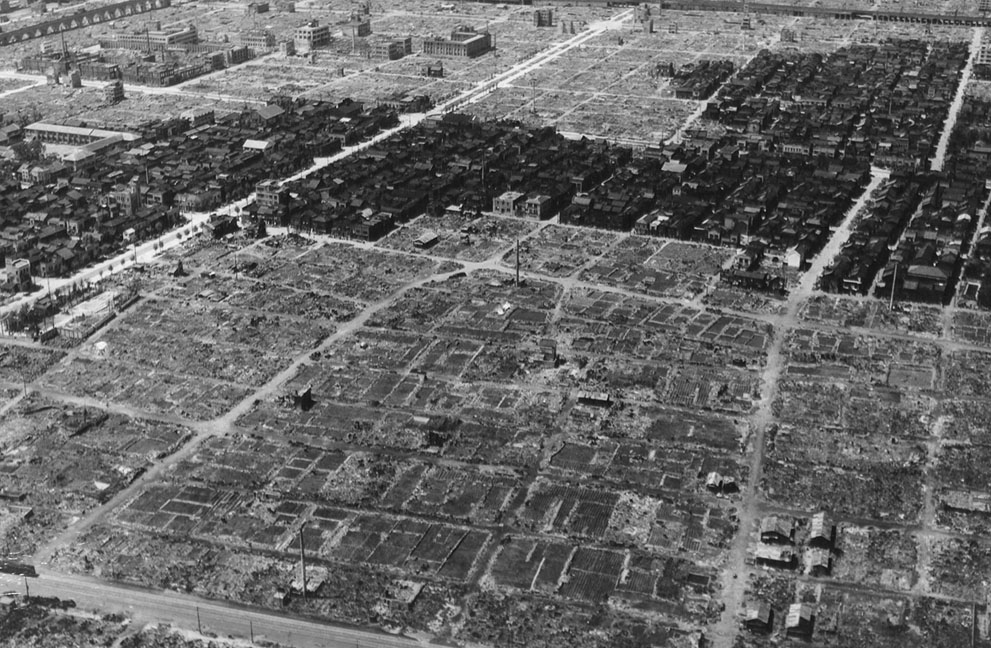
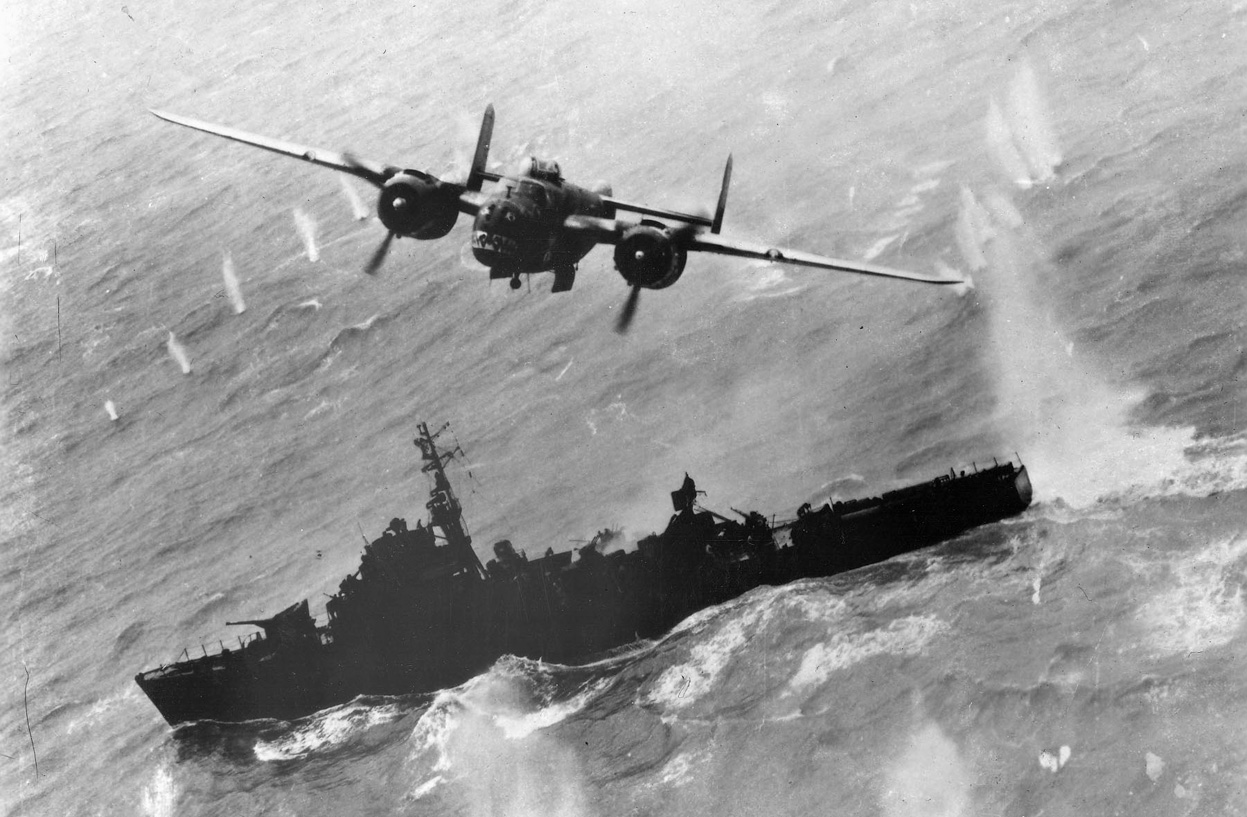
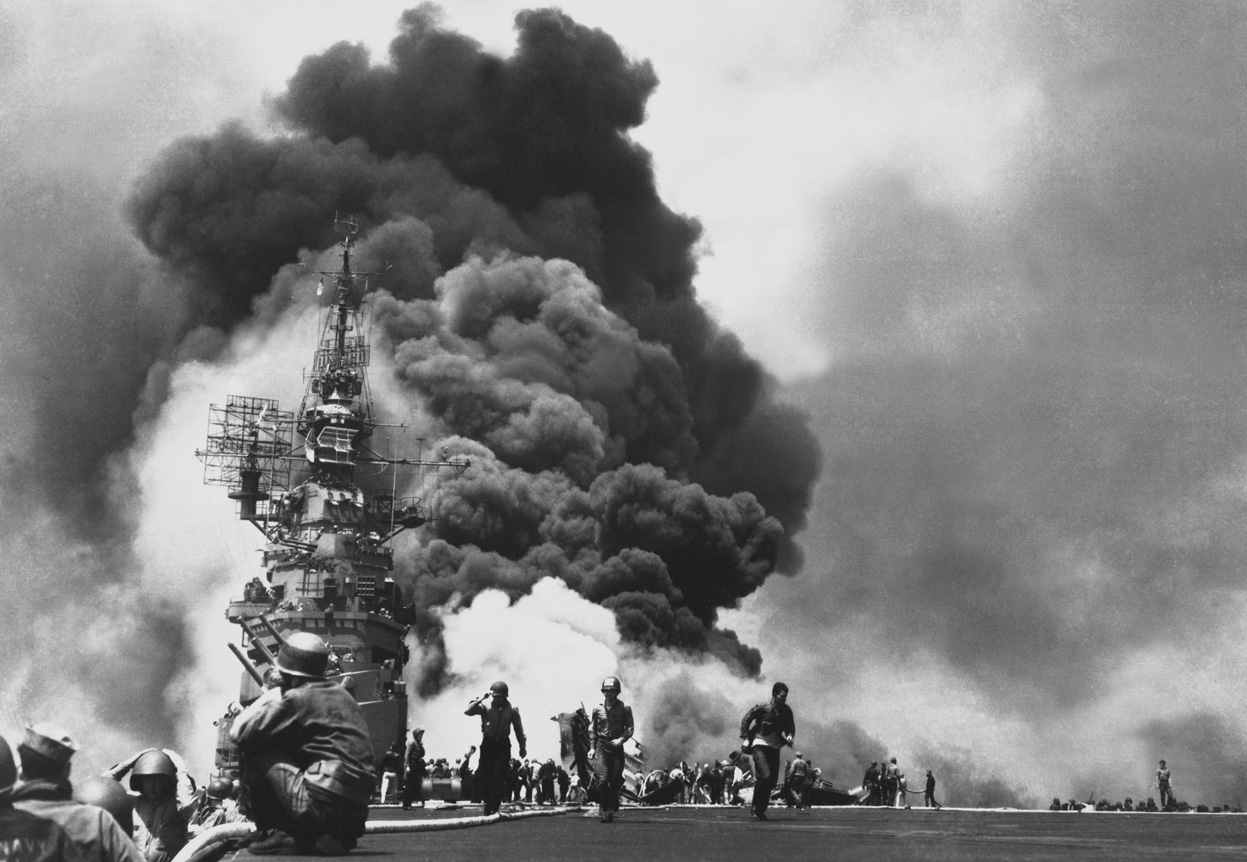
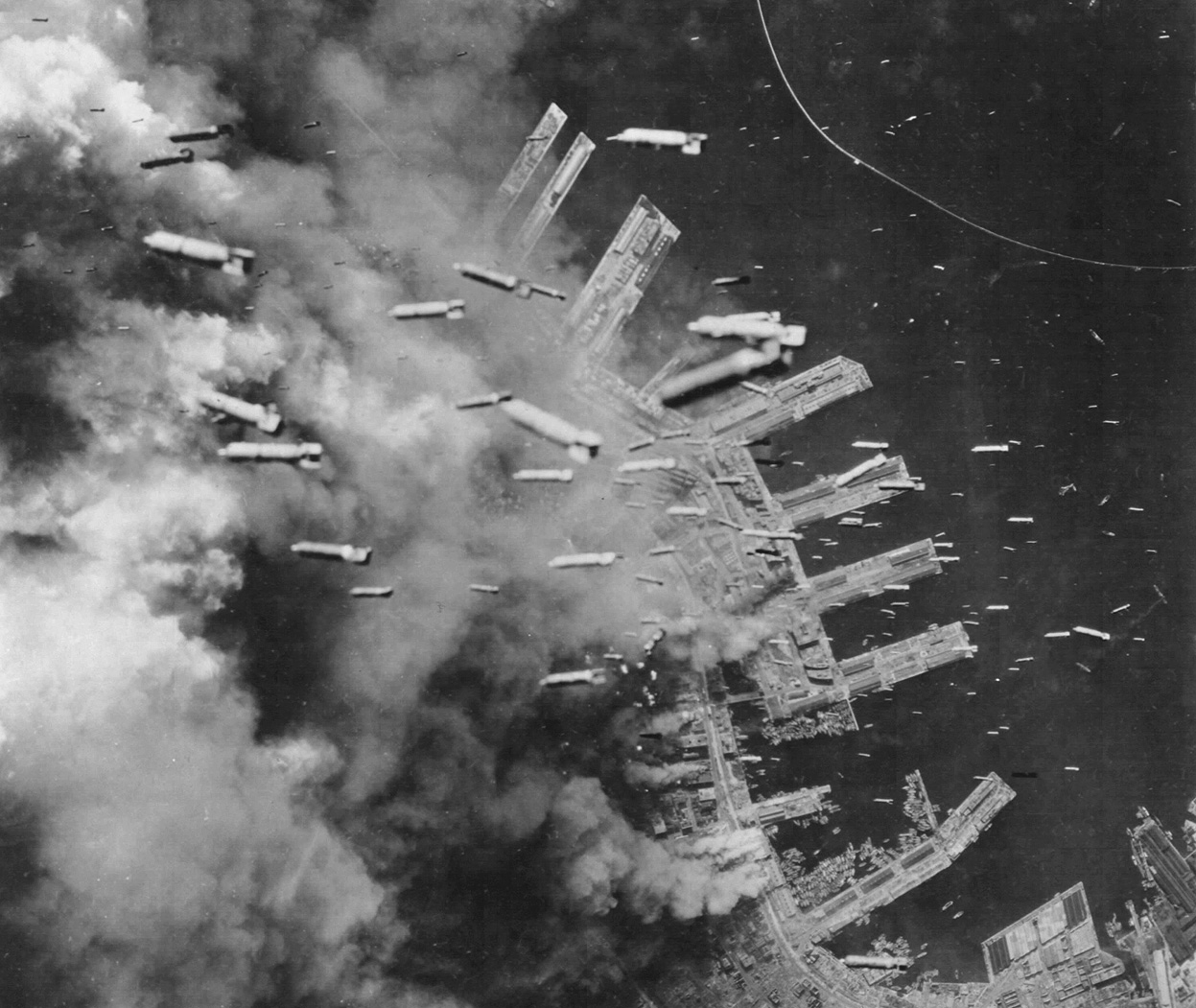
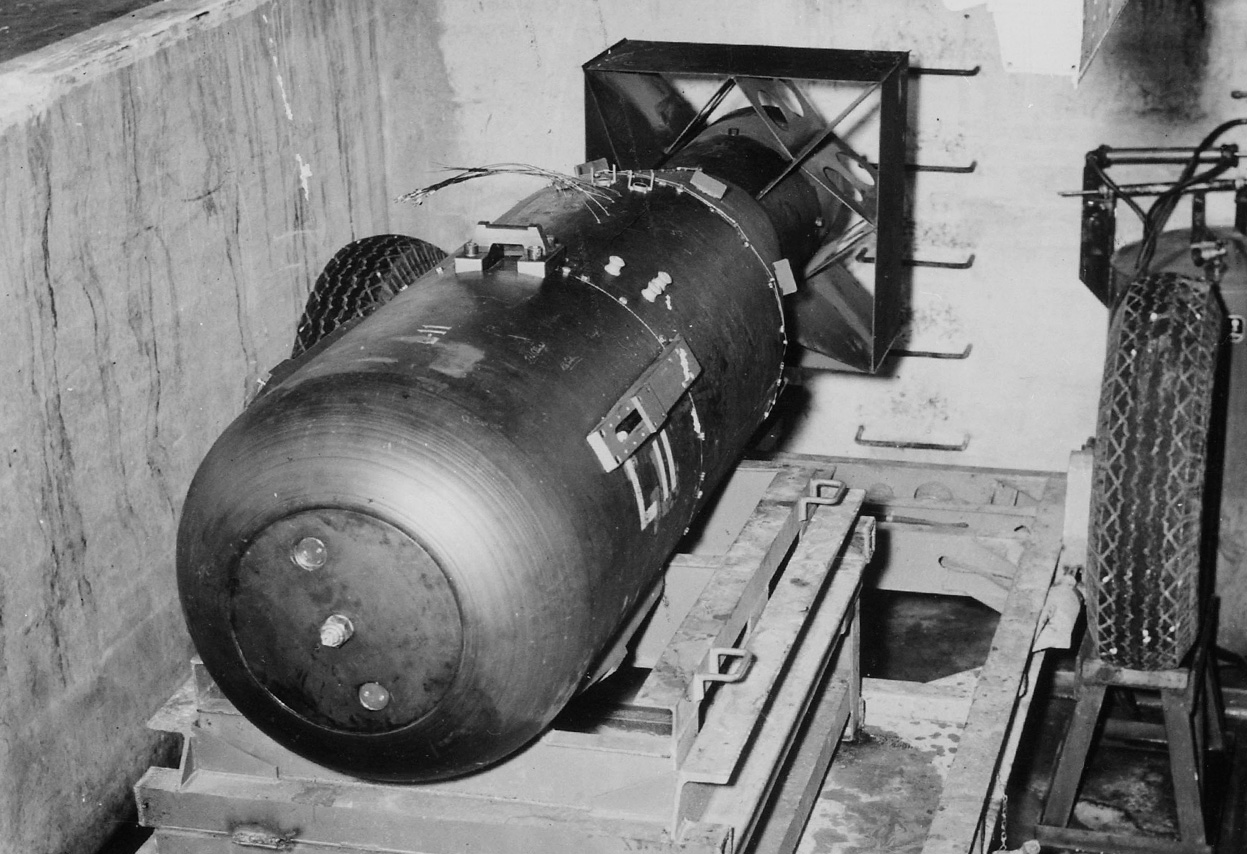
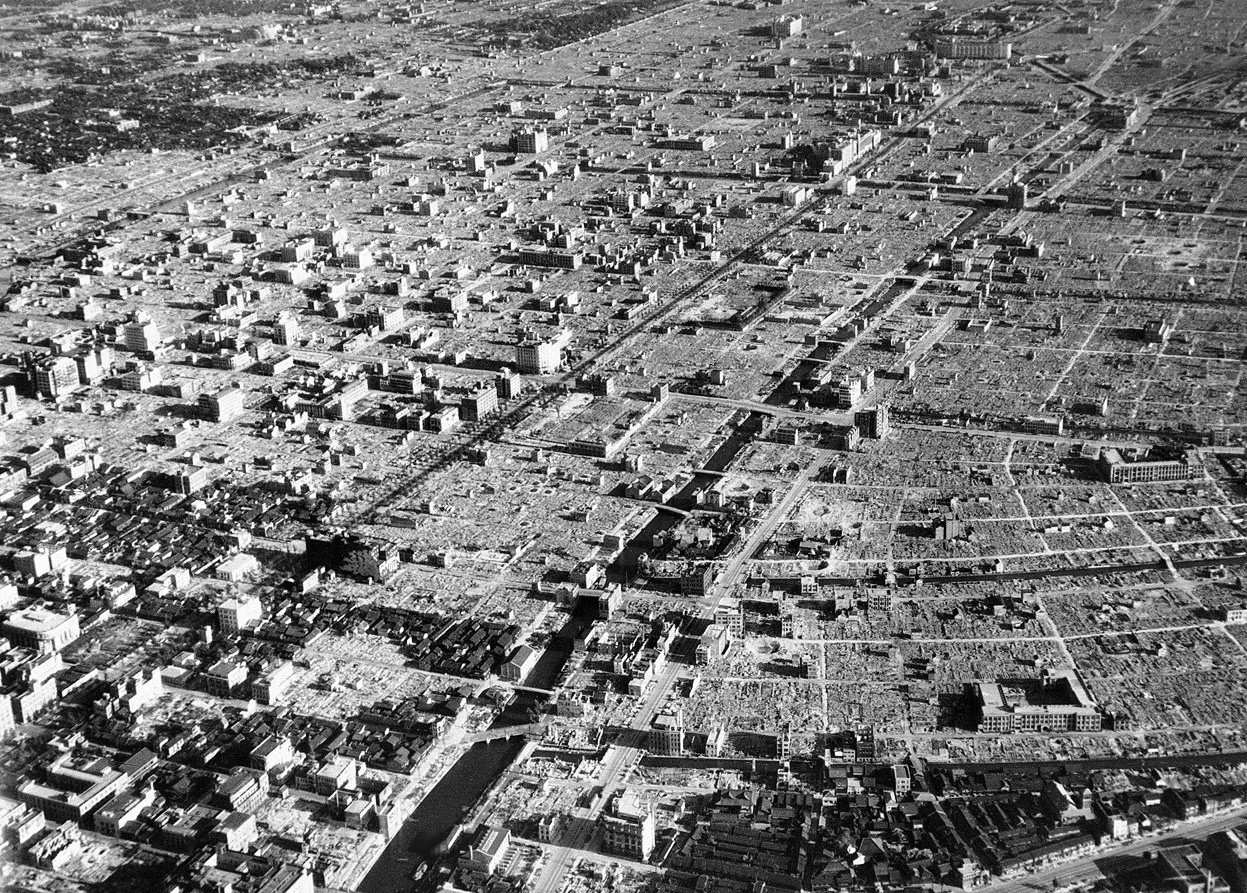




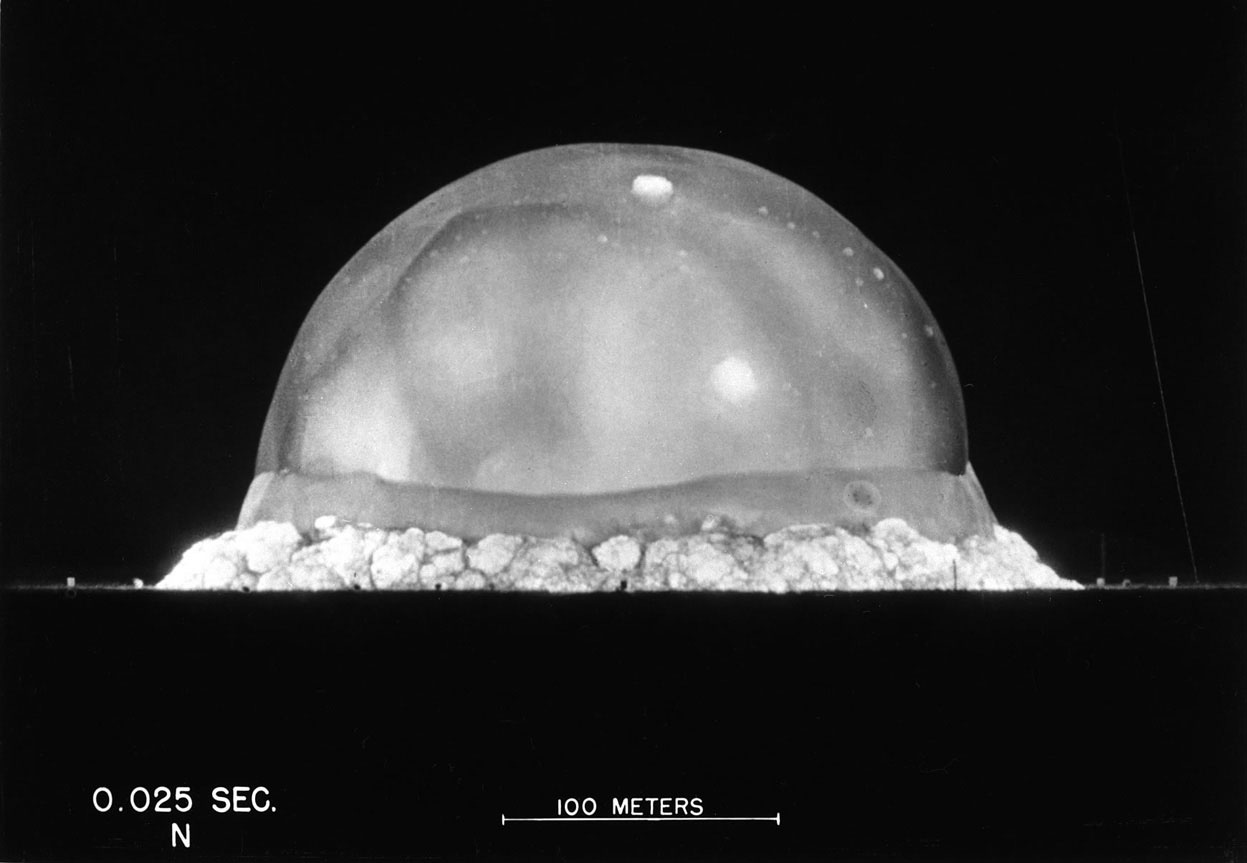



Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The United States gave Japan a warning and a deadline to surrender before the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, though not with an explicit mention of the atomic bomb itself.
Key Warning: The Potsdam Declaration (July 26, 1945)
- The Potsdam Declaration was issued by the United States, the United Kingdom, and China.
- It called for Japan’s unconditional surrender, warning of “prompt and utter destruction” if they refused.
- It did not mention the atomic bomb specifically, as the weapon had not yet been used publicly and was still secret.
- Japan was given an ultimatum, though no exact deadline date was specified.
- Japan’s government rejected the ultimatum (or more accurately, chose to ignore it, which was interpreted as rejection by the Allies).
What happened next:
- On August 6, 1945, the U.S. dropped the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima.
- On August 8, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan.
- On August 9, the second atomic bomb was dropped on Nagasaki.
- Japan announced its intention to surrender on August 15, 1945, leading to the formal surrender on September 2, 1945.
Summary:
The U.S. did issue a surrender ultimatum (Potsdam Declaration) before the bombings, but did not reveal that an atomic bomb would be used. The warning was serious but vague about the nature of the coming destruction.
747815257647595520
747124089272107008
Here are some other average salaries for U.S. Army enlisted soldiers.
704114929525030912







695784200954052608
George Carlin on War
675486202737098752
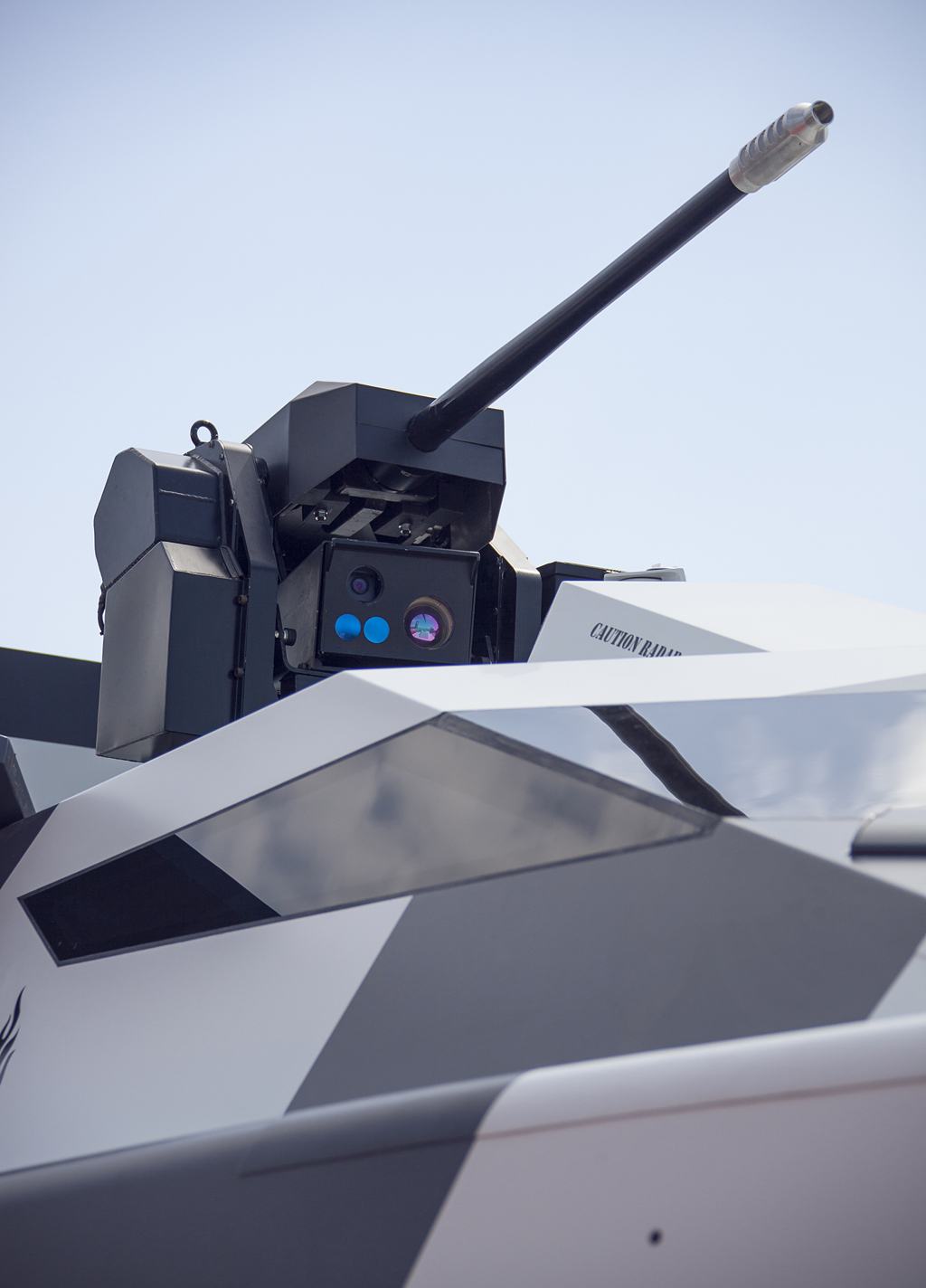

BAE Systems – LEMUR30 Remote Weapon System
145171031496
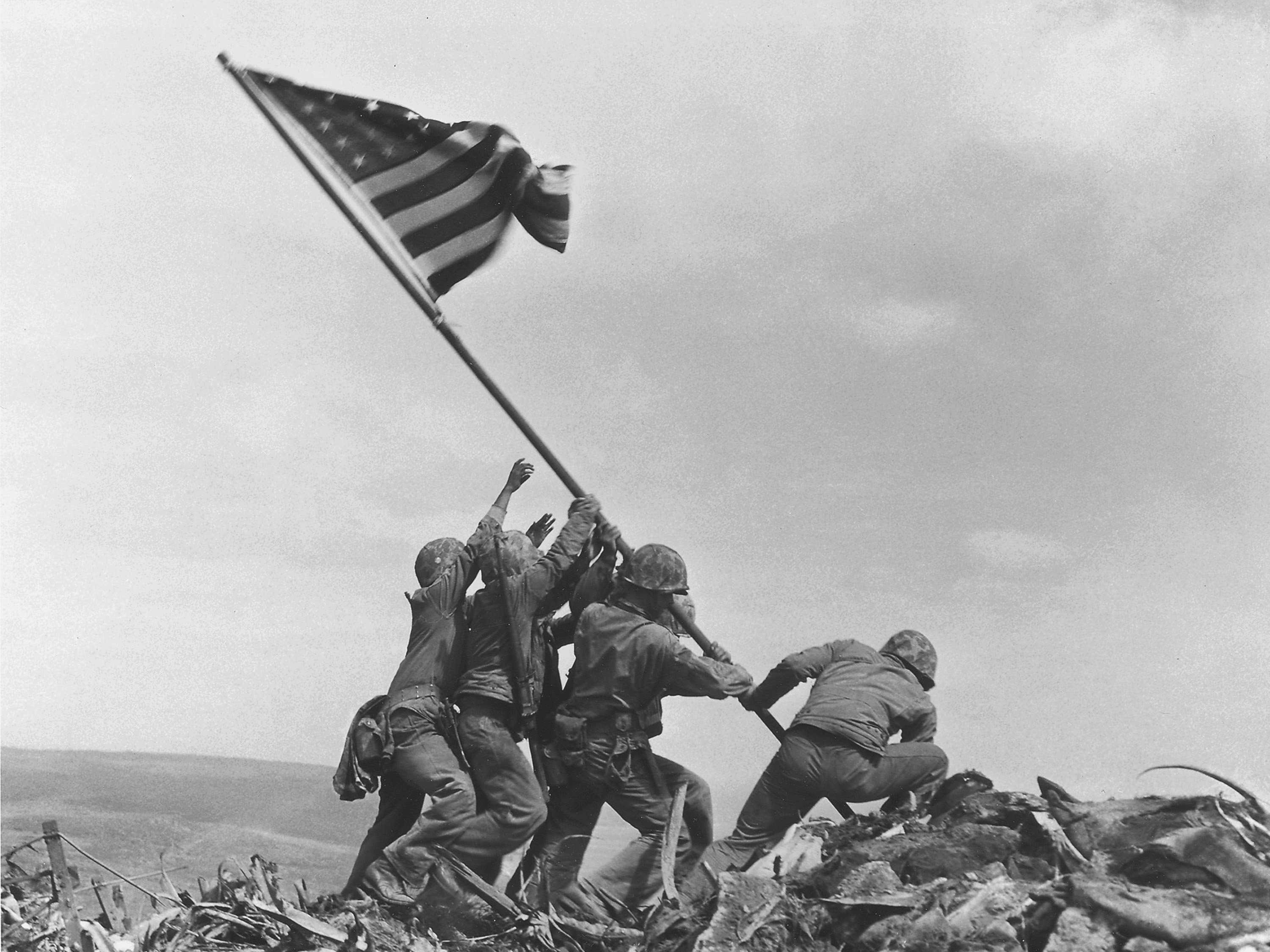

The raising of the flag at Iwo Jima